Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
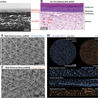
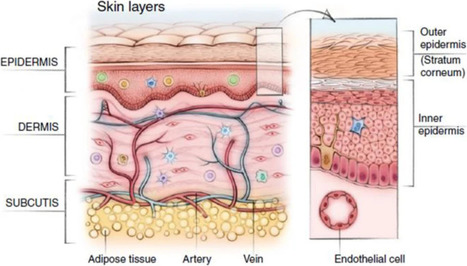
A recent collaboration between researchers at the University of Oregon (UO) and L’Oréal has resulted in the development of a multilayered artificial skin model, designed to resemble the complexity of real human skin closely. This achievement has implications for improving the testing of skin care products and potentially enhancing skin healing methods. Led by Associate Professor Paul Dalton from the Phil and Penny Knight Campus for Accelerating Scientific Impact at the UO, the research relies on Dalton’s novel 3D printing technique. Published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, this technique enables the creation of a two-layered artificial skin, with each layer separated by a membrane, mirroring the structure of natural skin.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
The World Health Organization, along with Bill Gates and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are pushing for vaccine patches to be mailed directly to people’s homes. The rulers will stop at nothing to ensure as many humans as possible are injected with mRNA technology and use Big Pharma and its drugs.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Queensland is one step closer to producing needle-free vaccine patches, with biotechnology giant Vaxxas estimating they are three to five years away from releasing their first commercial product. Attending the Hamilton facility’s opening on Monday morning, Deputy Premier Steven Miles said the technology would be a “game changer” to healthcare delivery in Australia and the world.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
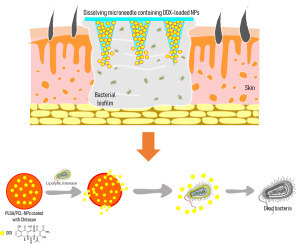
The presence of bacterial biofilms in wounds is a main issue in the healing process. Conventional therapy of bacterial biofilms is hampered by the poor penetration of antibacterial agents through the physical barrier on the infected skin and the non-specific target of antibacterial agents.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
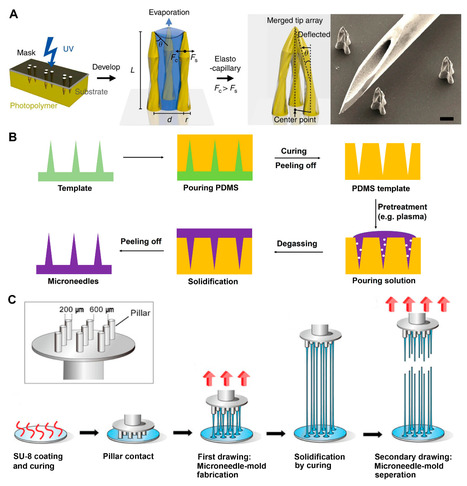
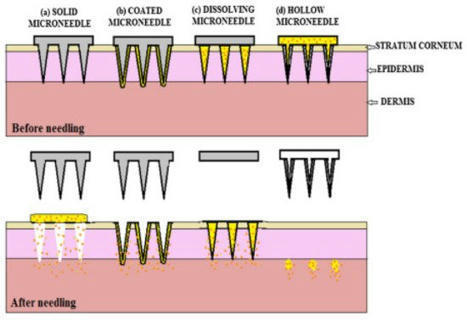
Conventional needle technologies can be advanced with emerging nano- and micro-fabrication methods to fabricate microneedles. Nano-/micro-fabricated microneedles seek to mitigate penetration pain and tissue damage, as well as providing accurately controlled robust channels for administrating bioagents and collecting body fluids. Here, design and 3D printing strategies of microneedles are discussed with emerging applications in biomedical devices and healthcare technologies.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Live webinar on 3D Microfabrication of microneedles for medical applications using rapid prototyping and direct 3D printing for series production. Register now

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
A startup under the umbrella of CU Innovation Hub in collaboration with the Chula Faculty of Science has developed an innovative “Detachable and Dissolvable Microneedle” that makes any injections easy and painless for everyone, while also significantly reducing medical wastes.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
A collaborative team, including scientists from the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), has developed a novel microneedle for injecting therapeutics into the eyes, potentially solving one of the major challenges of treating eye diseases – accurate delivery of therapeutic drugs to the retina, while guarding against possible complications at the injection site.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Nanoneedle start-ups are traversing the biotech valley of death — from fundamental university research into commercial development in advanced therapeutics and diagnostics. How can academics make the most of this opportunity?

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
In this study, a modified, HexaPro S protein subunit vaccine, delivered using a needle-free high-density microarray patch (HD-MAP), was investigated for its immunogenicity and virus-neutralizing abilities. Mice given two doses of the vaccine candidate generated potent antibody responses capable of neutralizing the parental SARS-CoV-2 virus as well as the variants of concern, Alpha and Delta. These results demonstrate that this alternative vaccination strategy has the potential to mitigate the effect of emerging viral variants.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
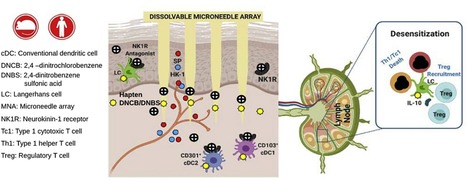
Our findings demonstrate that immune-regulation by engineering localized skin neuroimmune networks can be used to treat cutaneous diseases that like CD, are caused by type-1 immunity.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Researchers and biotechnology company Vaxxas are studying if the new delivery technology, called a high-density microarray patch, can protect participants from diseases including measles and rubella. If successful, the needle-less technology could be used for a number of other vaccinations including influenza and COVID-19.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
A need-based layered dissolving microneedle system loading tacrolimus (TAC) and diclofenac sodium (DIC) in different layers specifically delivers TAC and DIC to skin and articular cavity, simultaneously alleviating psoriatic skin and arthritic joint lesions.
|

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
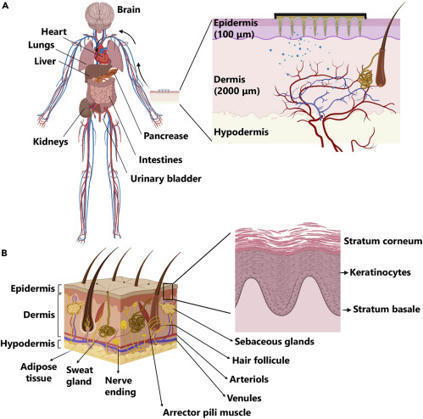
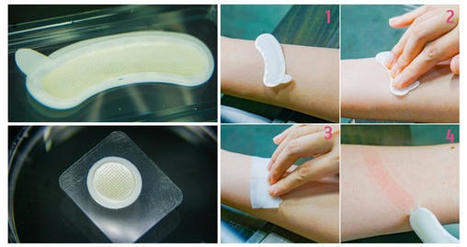
Various non-invasive administrations have recently emerged as an alternative to conventional needle injections. A transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) represents the most attractive method among these because of its low rejection rate, excellent ease of administration, and superb convenience and persistence among patients. TDDS could be applicable in not only pharmaceuticals but also in the skin care industry, including cosmetics. Because this method mainly involves local administration, it can prevent local buildup in drug concentration and nonspecific delivery to tissues not targeted by the drug. However, the physicochemical properties of the skin translate to multiple obstacles and restrictions in transdermal delivery, with numerous investigations conducted to overcome these bottlenecks.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
The vaccine patches being developed by Vaxxas are part of an emerging technology known as microneedle vaccines. This technology offers the convenience of self-administration, enabling vaccine manufacturers to deposit their vaccinations through the surface of the skin in mere seconds. Moreover, the patches can remain stable at room temperature, eliminating the need for cold chain storage.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
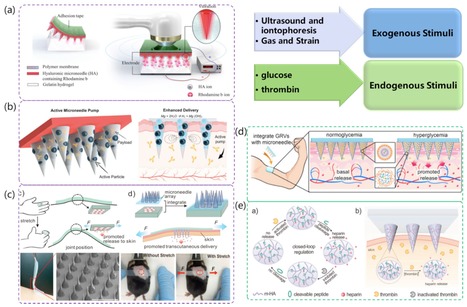
Microneedle (MN) technology is a rising star in the point-of-care (POC) field, which has gained increasing attention from scientists and clinics. MN-based POC devices show great potential for detecting various analytes of clinical interests and transdermal drug delivery in a minimally invasive manner owing to MNs’ micro-size sharp tips and ease of use. This review aims to go through the recent achievements in MN-based devices by investigating the selection of materials, fabrication techniques, classification, and application, respectively.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
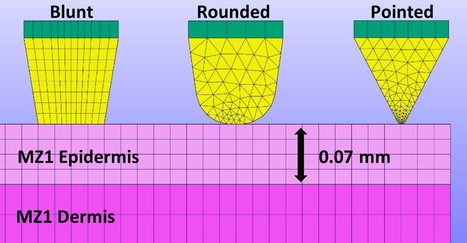
Microneedle (MN) array patches present a promising new approach for the minimally invasive delivery of therapeutics and vaccines. However, ensuring reproducible insertion of MNs into the skin is challenging. The spacing and arrangement of MNs in an array are critical determinants of skin penetration and the mechanical integrity of the MNs. In this work, the finite element method was used to model the effect of MN spacing on needle reaction force and skin strain during the indentation phase prior to skin penetration. Spacings smaller than 2–3 mm (depending on variables, e.g., skin stretch) were found to significantly increase these parameters.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Tattooing is a painful process that involves the introduction of artificial pigment under the skin. If not performed hygienically, tattoos can induce various health complications, including immune and inflammatory reactions, infections, and chronic skin defects such as dermatoses. Between 2% and 27% of individuals experience some sort of discomfort after having a tattoo, with 0.5-6% developing skin infections.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
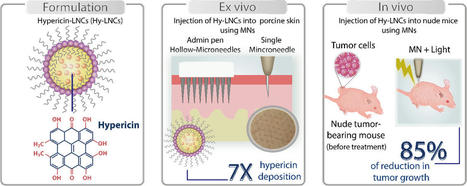
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) to manage non-melanoma skin cancers has garnered great attention over the past few years. Hypericin (Hy) is a potent lipid-soluble photosensitiser with promising anticancer therapeutic activities. Nevertheless, its poor water-solubility, aggregation in biological systems and insufficient skin penetration restricted its effective exploitation. Herein, we report for the first-time encapsulation of Hy into lipid nanocapsules (Hy-LNCs), and then application of an AdminPen™ hollow microneedles (Ho-MNs) array and an in-house fabricated Ho-MN to enable efficient intradermal delivery.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Microneedle (MNs) technology is a recent advancement in biomedical science across the globe. The current limitations of drug delivery, like poor absorption, low bioavailability, inadequate skin permeation, and poor biodistribution, can be overcome by MN-based drug delivery. Nanotechnology made significant changes in fabrication techniques for microneedles (MNs) and design shifted from conventional to novel, using various types of natural and synthetic materials and their combinations. Nowadays, MNs technology has gained popularity worldwide in biomedical research and drug delivery technology due to its multifaceted and broad-spectrum applications. This review broadly discusses MN’s types, fabrication methods, composition, characterization, applications, recent advancements, and global intellectual scenarios.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
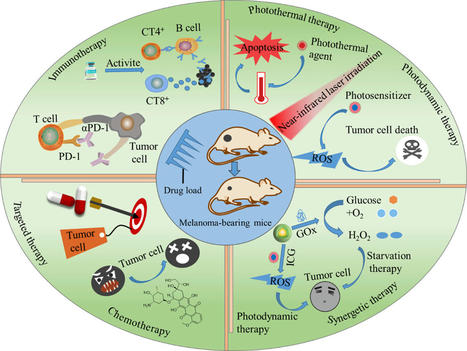
As an emerging drug delivery system, microneedles (MNs) can efficiently deliver drugs through the skin, increase the drug distribution in deeper tumor sites and minimize the leakage of therapeutic drugs into adjacent tissues, thus improving the therapeutic effect. In addition, compared with traditional drug delivery methods, MN-based drug delivery system has the advantages of simplicity, safety and little pain.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
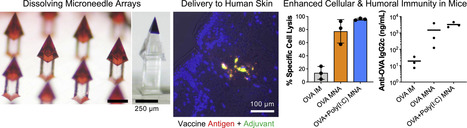
Cutaneous vaccination of mice using these MNAs induces more potent antigen-specific cellular and humoral immune responses than those elicited by traditional intramuscular injection. Together, the unique geometric features of these undercut MNAs and the associated manufacturing strategy, which is compatible with diverse drugs and biologics, could enable a broad range of non-cutaneous and cutaneous drug delivery applications, including multicomponent vaccination.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Light-based therapy is an emerging treatment for skin cancer, which has received increased attention due to its drug-free and non-invasive approach. However, the limitation of current light therapy methods is the inability for light to penetrate the skin and reach deep lesions. As such, we have developed a polylactic acid (PLA) microneedles array as a novel light transmission platform to perform in vitro evaluation regarding the effect of light therapy on skin cancer. For the first time, we designed and fabricated a microneedle array system with a height fixation device that can be installed in a cell culture dish and an LED array for blue light irradiation. The effect of the blue light combined with the microneedles on cell apoptosis was evaluated using B16F10 melanoma cells and analyzed by Hoechst staining. Our results demonstrate that blue light can be transmitted by microneedles to skin cells and effectively affect cell viability

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Experiments using this groundbreaking invention on mice with cancers have shown that the animals’ immune responses were much better than those seen in conventional vaccination methods. The technology paves the way for developing an easy-to-use cell therapy and other therapeutics against cancers and other diseases. Made from a cryogenic solution, these icy microneedles are less than 1mm long and can deliver living mammalian cells into the skin. The device is like a skin patch and the microneedles can detach from the patch base, melt and then penetrate the skin.

|
Scooped by
Beeyond
|
Silk fibroin has been widely used as fundamental components for the construction of biocompatible flexible electronics, particularly for wearable and implantable devices. Furthermore, in recent years, more attention has been paid to the investigation of the functional characteristics of silk fibroin, such as the dielectric properties, piezoelectric properties, strong ability to lose electrons, and sensitivity to environmental variables. Here, this paper not only reviews the preparation technologies for various forms of silk fibroin and the recent progress in the use of silk fibroin as a fundamental material but also focuses on the recent advanced works in which silk fibroin serves as functional components. Additionally, the challenges and future development of silk fibroin-based flexible electronics are summarized.
|
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...
 Your new post is loading...
Your new post is loading...